Installation
This project aims to both find the determinants of the DX Gap in TB, and to generalise these methods into a broader R package framework for other diseases. This creates the need for a project structure that both allows for a high-level of reproducibility (using exact R package versions to reproduce analyses calculating determinants) and for generalisability (so that the methods work across different R package versions in the future).
To achieve reproducibility, the renv package is used to create a reproducibile environment. Take this approach when you want to exactly reproduce any analyses performed as part of this project. To use this project with renv:
- Clone the package with HTTPS/SSH.
- If this is your first time running the project,
renvshould automatically bootstrap itself, downloading and installing the appropriate version of renv. - You will then be prompted to download and install all the packages needed by running
renv::restore().
To achieve generalisability and to install this project as an R package, the DESCRIPTION file is used to specify package dependencies. Take this approach when you want to use the functions and ideas within the package. You can install the development version of find.dxgap from GitHub with:
# install.packages("devtools")
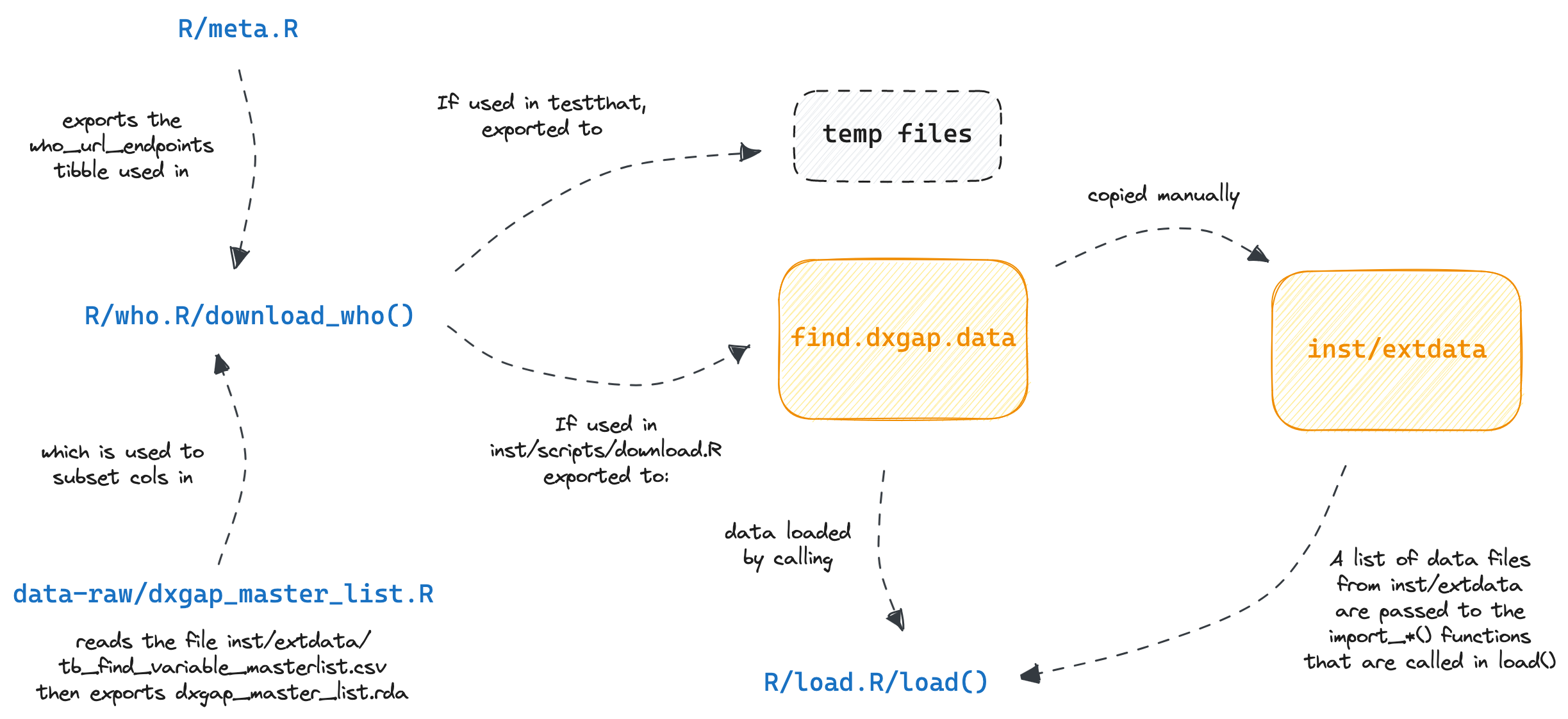
devtools::install_github("finddx/find.dxgap")find.dxgap.data
Clone find.dxgap.data to get data for the project.
The following env. variable needs to be set to establish connection between find.dxgap and find.dxgap.data. Please call, usethis::edit_r_environ(scope = "user") and c/p the following in your .Renviron file:
Usage
Tables
Once DXGAP_DATADIR is set, build a wide table for given year and disease:
tb_vars <- c(
"year", "country", "is_hbc", "country_code", "who_dx_gap", "pop_total",
"pop_urban_perc", "pop_density", "gdp", "c_newinc", "e_inc_num",
"e_mort_100k", "culture", "smear", "xpert", "m_wrd"
)
build_tbl("tb", year = 2019, vars = tb_vars)
#> # A tibble: 190 × 15
#> year is_hbc country_code dx_gap pop_total pop_urban_perc pop_density gdp
#> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2019 1 AGO 35.0 3.24e7 66.2 26.0 6.93e10
#> 2 2019 1 BGD 20.3 1.66e8 37.4 1272. 3.51e11
#> 3 2019 1 BRA 10.9 2.12e8 86.8 25.3 1.87e12
#> 4 2019 1 CAF 57.0 5.21e6 41.8 8.36 2.22e 9
#> 5 2019 1 CHN 11.8 1.41e9 60.3 150. 1.43e13
#> 6 2019 1 COD 38.0 8.99e7 45.0 39.7 5.18e10
#> 7 2019 1 COG 43.8 5.57e6 67.4 16.3 1.28e10
#> 8 2019 1 ETH 30.6 1.14e8 21.2 101. 9.59e10
#> 9 2019 1 GAB 55.0 2.24e6 89.7 8.70 1.69e10
#> 10 2019 1 IDN 33.5 2.70e8 56.0 144. 1.12e12
#> # ℹ 180 more rows
#> # ℹ 7 more variables: c_newinc <dbl>, e_inc_num <dbl>, e_mort_100k <dbl>,
#> # culture <dbl>, smear <dbl>, xpert <dbl>, m_wrd <dbl>Alternatively, one can override the supported estimated and notified cases for given disease (allowed for future implementations).
build_tbl(
"tb",
year = 2019,
estimated = "who_estimates.e_inc_num",
notified = "who_notifications.c_newinc",
vars = tb_vars
)
#> # A tibble: 190 × 15
#> year is_hbc country_code dx_gap pop_total pop_urban_perc pop_density gdp
#> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2019 1 AGO 35.0 3.24e7 66.2 26.0 6.93e10
#> 2 2019 1 BGD 20.3 1.66e8 37.4 1272. 3.51e11
#> 3 2019 1 BRA 10.9 2.12e8 86.8 25.3 1.87e12
#> 4 2019 1 CAF 57.0 5.21e6 41.8 8.36 2.22e 9
#> 5 2019 1 CHN 11.8 1.41e9 60.3 150. 1.43e13
#> 6 2019 1 COD 38.0 8.99e7 45.0 39.7 5.18e10
#> 7 2019 1 COG 43.8 5.57e6 67.4 16.3 1.28e10
#> 8 2019 1 ETH 30.6 1.14e8 21.2 101. 9.59e10
#> 9 2019 1 GAB 55.0 2.24e6 89.7 8.70 1.69e10
#> 10 2019 1 IDN 33.5 2.70e8 56.0 144. 1.12e12
#> # ℹ 180 more rows
#> # ℹ 7 more variables: c_newinc <dbl>, e_inc_num <dbl>, e_mort_100k <dbl>,
#> # culture <dbl>, smear <dbl>, xpert <dbl>, m_wrd <dbl>Optionally, a time series can be built:
build_tbl(
"tb",
year = NULL,
estimated = "who_estimates.e_inc_num",
notified = "who_notifications.c_newinc",
vars = tb_vars
)
#> # A tibble: 1,140 × 15
#> year is_hbc country_code dx_gap pop_total pop_urban_perc pop_density gdp
#> <dbl> <dbl> <chr> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2016 1 AGO 43.9 29154746 64.1 23.4 4.98e10
#> 2 2017 1 AGO 49.6 30208628 64.8 24.2 6.90e10
#> 3 2018 1 AGO 40.4 31273533 65.5 25.1 7.78e10
#> 4 2019 1 AGO 35.0 32353588 66.2 26.0 6.93e10
#> 5 2020 1 AGO 42.6 33428486 66.8 26.8 5.02e10
#> 6 2021 1 AGO 44.9 34503774 67.5 27.7 6.57e10
#> 7 2016 1 BGD 37.0 159784568 35.1 1228. 2.65e11
#> 8 2017 1 BGD 32.2 161793964 35.9 1243. 2.94e11
#> 9 2018 1 BGD 26.2 163683958 36.6 1257. 3.21e11
#> 10 2019 1 BGD 20.3 165516222 37.4 1272. 3.51e11
#> # ℹ 1,130 more rows
#> # ℹ 7 more variables: c_newinc <dbl>, e_inc_num <dbl>, e_mort_100k <dbl>,
#> # culture <dbl>, smear <dbl>, xpert <dbl>, m_wrd <dbl>An error is raised, if a disease is not supported yet:
build_tbl("covid", year = NULL, vars = tb_vars)
#> Error in `check_supported_disease()`:
#> ! `covid` not in `dxgap_diseases`.
#> ✖ Disease is not supported yet.A “disease-table” returned from build_tbl() respects the following criteria:
- Contains only records for which is possible to compute the “dx_gap”.
- In case of time series, a consistent set of “high-burden” countries across years is returned.
To read and tidy any table:
import_tbl("who_hbc_2023-07-28.csv")
#> # A tibble: 300 × 3
#> share_global_inc country_code year
#> <dbl> <chr> <dbl>
#> 1 83 AGO 2016
#> 2 83 AGO 2017
#> 3 83 AGO 2018
#> 4 83 AGO 2019
#> 5 83 AGO 2020
#> 6 83 BGD 2016
#> 7 83 BGD 2017
#> 8 83 BGD 2018
#> 9 83 BGD 2019
#> 10 83 BGD 2020
#> # ℹ 290 more rows
import_tbl("gf_procurement_2023-07-26.csv")
#> # A tibble: 199 × 3
#> country_code year total_numb_device
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 AFG 2020 55000
#> 2 AFG 2021 90800
#> 3 AGO 2020 30000
#> 4 AGO 2021 43890
#> 5 AGO 2022 11000
#> 6 ALB 2019 2002
#> 7 ARM 2020 300
#> 8 ARM 2023 4500
#> 9 AZE 2021 16500
#> 10 AZE 2022 9806
#> # ℹ 189 more rowsPlease, refer to find.dxgap.data for the available tables.
Report
Few templates have been implemented for data exploration:
view_templates() |>
writeLines()
#> eda.Rmd
#> eda_ts.Rmd
#> explain_lm.Rmd
#> missing.Rmd
render_report(
"eda_ts.Rmd",
disease = "tb",
year = NULL, # the template requires `NULL`
interactive = TRUE,
vars = tb_vars
)
render_report(
"explain_lm.Rmd",
disease = "tb",
year = 2019, # the template requires a year to be selected
interactive = TRUE,
vars = tb_vars
)Objectives of the project
Support in data analysis / processing for the development of a Shiny dashboard (TB Diagnostics Policy dashboard) that will show by country the:
TB diagnostic landscape
TB burden
More specifically it will show:
- Countries with similar demographics to improve the learning of algorithms
- Need for testing by region and test type
- Assess readiness and willingness of countries for new upcoming TB diagnostics
- Understand Gap in testing and TB incidence in a country
- Assess existing association between algorithms and TB incidence / % of cases bacteriologically confirmed